URL :

Nowadays, concerns about the outbreak of pandemic new infectious diseases have been deepened because of population shift, climate change, aging, and etc. The emergence and spread of new infectious diseases not only threaten the health of individuals, but also cause social and economic crisis. Thus, it needs for us to have a research environment which can effectively respond to infectious diseases from abroad. Research environment is also essential to support basic research, clinical research, and epidemiological studies to develop diagnostic devices, vaccines, and treatment. However, it is obviously difficult to secure research resources; therefore, it is essential to collaborate with foreign institutions to secure human resources and pathogen resources. And furthermore, it is significant to share research results.
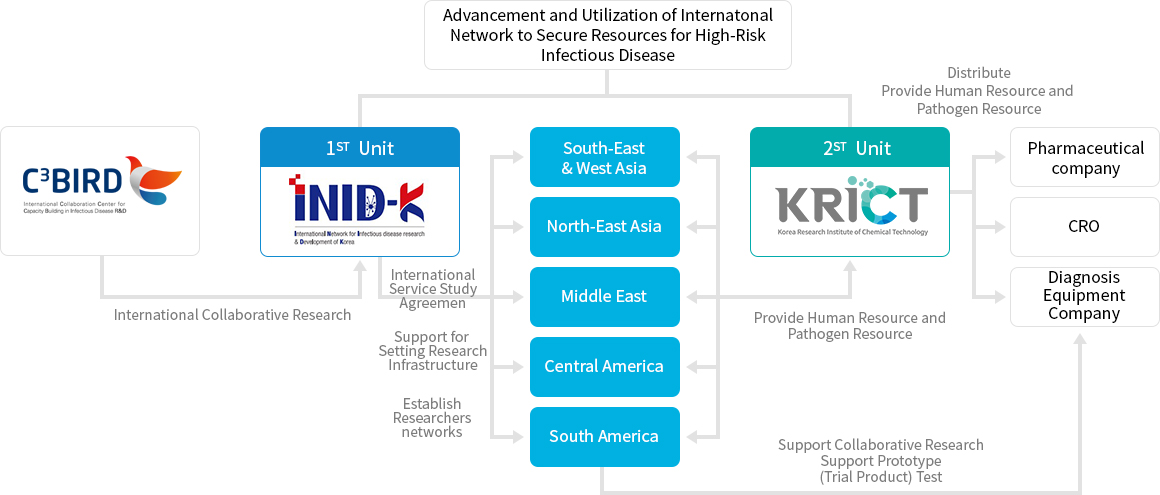
The full name of this research is ‘Advancement and Utilization of International Network to Secure Resources for High-Risk Infectious Disease’, and the research period is from November 2020 to December 2024. INID-K (International Network for Infectious Disease Research & Development of Korea) is the abbreviated name in English with 6 key words. Specifically, it is a new project that professor SeungHwan Lee from Seoul National University Hospital conducts as a principal investigator with Korea Research Institute Chemical Technology (KRICT) following Korean International Cooperation for Infectious Diseases (KOICID) research. It mainly aims to establish resource bank with human resources and pathogen resources through the advancement of the international network for high-risk infectious diseases. Furthermore, we intend to support research and secure the capacity to respond to infectious diseases. In particular, we expect three outcomes from this research as follows:
First of all, we aim to acquire basic knowledge and to establish fundamental source technology which contribute to prevent the inflow and spread of infectious diseases. Also, we support to conduct basic/translational/clinical trials in advance to prepare new infectious disease from foreign countries. Through those information and technologies accumulated in advance, it is expected that prompt development of diagnostic devices, vaccines, and treatments.
Secondly, we intend to minimize the economic loss and social anxiety caused by the inflow and spread of infectious diseases from abroad. With the international cooperative network and researchers from each institution, we plan to collect information on infectious diseases precisely and rapidly by country. At this time, we share that information for both the domestic researchers and government institution to establish domestic infection response system and to the national epidemiological research. In the event of an actual infection, it will be used to set up the complementary cooperative system with various countries.
Lastly, we plan to contribute to the growth of the domestic pharmaceutical bio industry by commercializing diagnostic devices, vaccines, and treatments. We utilize the local research infrastructure and manpower from the international cooperative network to conduct this research. Also, we support basic/translational/clinical research for domestic researchers through this research. Moreover, basic and translational studies are conducted in local using human resources and pathogen resources which are difficult to secure in Korea. Based on the multi-national clinical trials, it is expected to be able to utilize diagnostic devices, treatments, and vaccines efficiently.